Understanding Your Dog’s Whining
Dogs use whining as a form of communication, much like barking and growling. Whining can indicate a variety of things, including desires, excitement, pain, or stress. Whether or not you should respond to your dog’s whining depends on understanding its cause. Responding to whining with treats or attention might inadvertently encourage more whining, leading to an excessive behavior pattern. To address whining effectively, it’s important to interpret the behavior, address its root cause, and employ strategies to reduce it.
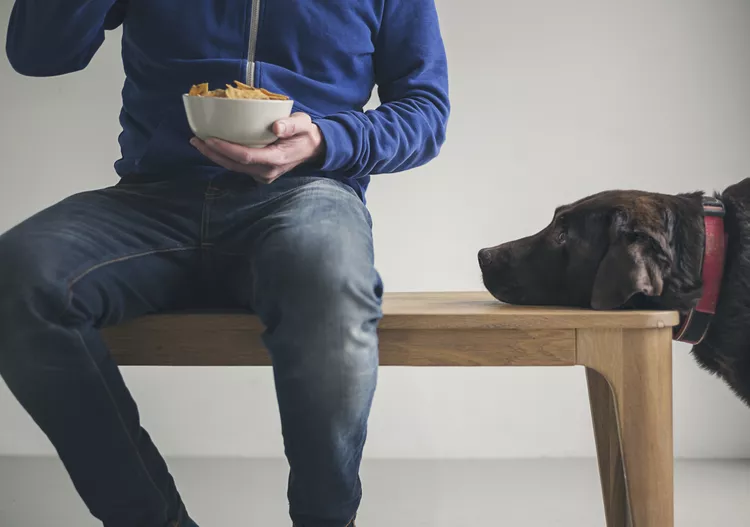

Why Is My Dog Whining?
Whining is particularly common in puppies who are still learning how to communicate their needs and feelings. Like human babies crying, puppies whine to get attention or food from their mother.
Often, the cause of whining is straightforward. Your dog might be asking for a treat, wanting to go outside, or seeking attention. However, sometimes the reason isn’t immediately clear. Observing accompanying body language can help you determine the cause. Common reasons for whining include:
- Requesting Something: If your dog wants something, such as a walk, food, or a toy, it might whine to express this desire. You might notice it looking between you and the object it wants.
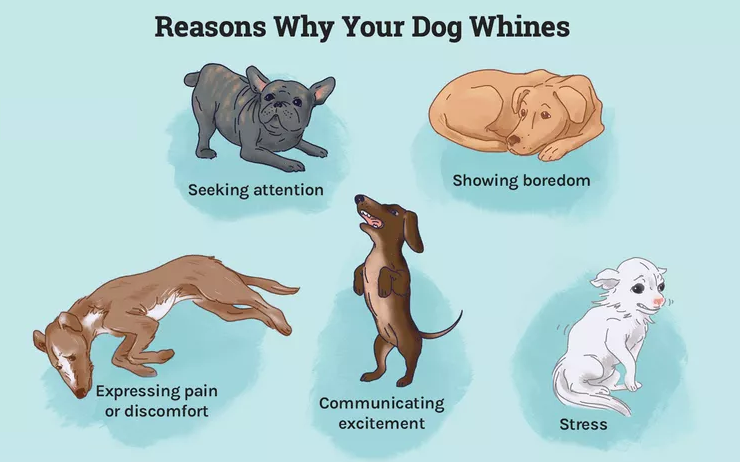
- Seeking Attention: Dogs may whine when they’re not the center of your attention, such as when you’re on the phone or focused on another task. This type of whining might also occur if your dog is feeling jealous of another person or pet.
- Communicating Excitement: Excited dogs might whine as part of their energetic display, often accompanied by jumping and running around. This type of whining can also be about seeking attention.
- Expressing Boredom: Bored dogs often whine with a “sigh-and-whine” pattern, signaling a lack of stimulation and a desire for interaction.
- Indicating Pain or Discomfort: If your dog is unwell or in pain, whining can be a way of alerting you to its discomfort. In some cases, this whining might be an attempt to self-soothe.
- Showing Stress: Dogs may whine when they’re anxious or scared. This type of whining is often accompanied by other stress-related behaviors, such as yawning, lip licking, or a tucked tail.
If your dog’s whining persists despite ruling out these common causes, a visit to the vet might be necessary to check for any underlying health issues.

How to Address Excessive Whining
To manage excessive whining, it’s crucial to understand the reason behind it before taking action. Some people may find occasional whining manageable, while others may find it bothersome and seek to minimize it. Here are some strategies:
- Identify the Type of Whine: Pay attention to the different sounds and pitches of whining to discern its cause. For instance, whining for attention may sound different from whining due to pain.
- Address Stress or Pain Carefully: If you suspect stress or discomfort, approach your dog gently. Avoid escalating the situation, as it could lead to increased anxiety or aggression.
- Avoid Punishment: Never punish or yell at your dog for whining. This can worsen anxiety and potentially lead to aggressive behavior.
- Find the Source of Anxiety: If the whining is due to fear or anxiety, identify and address the underlying cause. Desensitization and positive reinforcement can help your dog overcome its fears.
- Redirect and Reward: If your dog whines for attention or treats, redirect it to a different behavior, such as sitting or lying down, before providing a reward.
- Avoid Reinforcing Whining: Giving in immediately to whining can reinforce the behavior. Instead, wait for a moment of silence before offering attention or treats.
- Provide Enrichment: Ensure your dog has plenty of toys and regular exercise to prevent boredom and excess energy that can contribute to whining.
- Respond Selectively: Ignore whining when there is no apparent need and reward moments of silence to reinforce calm behavior.

In many cases, basic training, mental stimulation, and exercise can help reduce excessive whining. If the behavior remains problematic, consulting a professional trainer or behaviorist might be necessary. With patience and consistency, you can manage and reduce whining to a more manageable level.




